Marghab River
| Marghab River Murghab, Margab, Murqab, Margos, Margu, Margiana, Murgap | |
|---|---|
 The Marghab in the Badghis Province | |
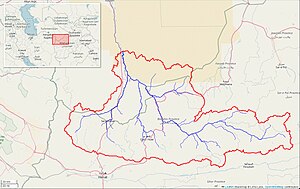 Marghab River watershed, upstream of Saryyazy Reservoir (Interactive map) | |
| Etymology | Persian Marv-ab,"River of Merv"[1][2] |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Countries | Afghanistan, Turkmenistan |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh, Marghab District, Afghanistan |
| • coordinates | 35°09′N 65°59′E / 35.15°N 65.99°E |
| Mouth | |
• location | Mary Oasis (ultimately the Aral Sea via Amu Darya) |
| Length | ~850 km (530 mi) |
| Basin size | 34,700 km2 (13,400 sq mi) (Harirod-Murghab basin)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 48.7 m3/s (1,720 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Amu Darya |
The Marghab River (Persian/Pashto: مرغاب, Murghāb, Balochi: مرگاپ), anciently the Margiana (Ancient Greek: Μαργιανή, Margianḗ), is an 850-kilometre (530 mi) long river in Central Asia. It rises in the Paropamisus Mountains (Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh) in Ghor Province, flows through the Marghab District in central Afghanistan, then runs northwest towards the Bala Murghab. Reaching the oasis of Mary in the Karakum Desert of Turkmenistan, the Marghab debouches into the Karakum Canal, a diversion of water from the Amu Darya. The catchment area of the Marghab is estimated at 46,880 square kilometres (18,100 sq mi).[4]
Geography
[edit]The Marghab River originates in the Ghor Province of central Afghanistan, on a plateau among the chain of mountains of Paropamisus, Gharjistan and Band-i Turkestan. In its higher course, the river runs from east to west, towards Mukhamedkhan, for about 300 kilometres (190 mi) in a narrow, steep valley measuring less than one kilometer in width, with narrow gorges in some places.
Between Darband-i Kilrekht and Mukhammedkhan, the Marghab crosses the western part of Band-i Turkestan, and then runs toward the northwest in a deep canyon. At Mukhammedkhan, it crosses the gorges of Jaokar. After this, the valley widens somewhat, gradually reaching a width of 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) in Turkmenistan. Beyond Mukhamedkhan, a small portion of the water of the Marghab is used for irrigation; approximately 10,000 hectares (25,000 acres) are irrigated from the Marghab in Afghanistan. The Marghab receives the waters of the Kaysar river on the right, then forms the border between Turkmenistan and Afghanistan over 16-kilometre (10 mi) length.
In Turkmenistan, close to Tagtabazar, the Marghab receives the Kashan River from the left bank, and 25 kilometres (16 mi) further, there is the confluence of the Kushk. Downstream of the confluence with the Kushk lies the Saryyazy reservoir, built in 1959, and expanded in 1978. The reservoir and its surrounding area is ecologically important for birds.[5] Reaching the oasis of Mary, the Marghab mingles its waters with those of the Karakum Canal, a diversion of water from the Amu Darya.
-
The fertile Marghab Valley in Afghanistan
-
A bridge across the Marghab in 1962
-
The generators of Hindu Kush hydro power plant (Гиндукушская ГЭС) on Marghab River soon after its completion in 1909 by the Hungarian Ganz Works. At the time, it was the largest hydro power generating station of the Russian Empire
Hydrometry: the flows at Tagtabazar
[edit]The flow of Marghab was observed during 50 years (1936–85) at Tagtabazar, a location in Turkmenistan about 30 kilometres (19 mi) after the Marghab leaves the Afghan territory, and a score of kilometers upstream of the confluence with the Kushk.[6] At Tagtabazar, average annual flow observed over this period was 48.7 cubic metres per second (1,720 cu ft/s) for an observed surface area of 34,700 square kilometres (13,400 sq mi), which is 74 percent of the totality of the catchment area of the river. The geographically-averaged hydrometric flow passing through this part of the basin, by far greatest from the point of view of the flow, thus reached the figure of 44.3 millimeters per annual, which is very appreciable in this particularly desiccated area.
Monthly mean flows of Murghab (in cubic meters per second) measured at the hydrometric station of Tagtabazar
Data calculated over 50 years

A 2021 study indicates that in the near term (by 2040), the Marghab's flow could fall by as much as one-third due to climate change, and by 40 percent by the end of the 21st century.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ Rawlinson, George (January 19, 2018). A Short History of Persia. Ozymandias Press. ISBN 9781531277079 – via Google Books.
- ^ Strange, G. Le (June 16, 2011). The Lands of the Eastern Caliphate. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107600140 – via Google Books.
- ^ https://www.moore.af/MediaLibsAndFiles/media/afghanistan.moore-global.com/files/Research/17-Afghanistan-Water-Management.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "Surface water resources in North Afghanistan". Archived from the original on July 23, 2011.
- ^ "BirdLife Data Zone". Retrieved 2023-11-20.
- ^ UNESCO - Bassin du Murghab - Station : Takhta-Bazar Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Didovets, Iulii; Lobanova, Anastasia; Krysanova, Valentina; Menza, Christoph; Babagalieva, Zhanna; Nurbatsina, Aliya; Gavrilenko, Nadejda; Khamidov, Vohid; Umirbekov, Atabek; Qodirov, Sobir; Muhyyew, Dowletgeldi; Hattermann, Fred Fokko (April 2021). "Central Asian rivers under climate change: Impacts assessment in eight representative catchments". Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies. 34 (100779): 100779. Bibcode:2021JHyRS..3400779D. doi:10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100779. hdl:10419/229441. S2CID 233532220.
External links
[edit]- Murgap river (Murghab river) marked on the OpenStreetMap
- Morghab River, in Encyclopædia Britannica
- Map of the province of Ghor, with trace of the flow of waterArchived 29 June 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- Map of vegetation cover in the province of Badghis, with trace of the flow of waterArchived 29 June 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- "Delft Hydraulics - Integrated Water Resources Management for the Sistan Closed Inland Delta - ANNEX B : Forecasting the Flow from Afghanistan - Page 18 : cartes hydrographiques d'Afghanistan" (PDF).[permanent dead link] (1.50 MB) (in English)



